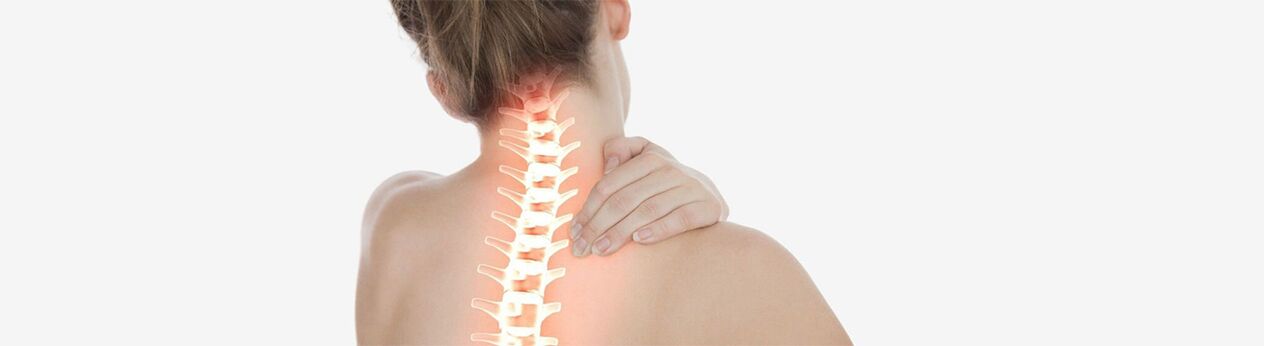
Cervical osteochondrosis is a chronic degenerative disease of articular cartilage tissues, most often occurs in the intervertebral discs of the spine, because they are more often exposed to high loads, which results in a decrease in elasticity, flattening and thinning of the discs located between the vertebrae, and then their bone tissueis replaced byAs the degenerative process progresses, surrounding structures become involved. This leads to the development of a whole complex of symptoms that deprives the patient of a comfortable life.
Why is cervical osteochondrosis dangerous?
Cervical osteochondrosis is pathological changes in the tissues of the intervertebral discs and the vertebrae themselves. Due to the thinning of soft tissues, the effect of wear of the vertebrae decreases, nerve fibers and blood vessels are compressed, the mobility of the cervical spine decreases, and head rotation is limited. As a result of this disease, blood circulation and blood supply to the brain deteriorates, migraines, headaches, tension, cluster headaches, heart rhythm disturbances, respiratory rhythm disturbances, deterioration of memory, vision, coordination and attention, intervertebral hernias, and brain damage occur. disorders and stroke develop.
Causes of osteochondrosis
What causes cervical osteochondrosis?
The development of cervical osteochondrosis is caused by a number of factors, each of which aggravates the course of the disease:
- Sedentary lifestyle (sedentary work);
- Excessive body weight;
- Incorrect posture;
- chronic diseases of the locomotor system that cause uneven distribution of the load on the spine (scoliosis, flat feet, x- and o-shaped deformations of the lower extremities);
- Congenital pathologies of the development of the spine;
- Excessive, repetitive stress on the spine;
- Hereditary tendency;
- Injuries.
Signs and symptoms
- Systemic dizziness;
- Pain in the back of the head, neck, collar area;
- Noise or ringing in the ears;
- A feeling of lack of air, inability to breathe deeply, severe shortness of breath develops;
- Nausea and vomiting, worse when trying to turn the head;
- Decreased visual acuity, flickering spots or fog in front of the eyes;
- Fluctuations in blood pressure that are difficult to correct with medication;
- Fainting due to vasospasm;
- Feeling of a lump in the throat, pain, dryness, swallowing problems, pain in the shoulder joint;
- Numbness of the fingers.
The degree of development of osteochondrosis
In the process of development of cervical osteochondrosis, four successive stages are distinguished, which determine the severity of symptoms and the general condition of the patient.
- Stage 1. The thickness of the intervertebral discs is slightly reduced. There are practically no symptoms, sometimes there is a slight discomfort in the neck, for example, when it is in an uncomfortable position for a long time.
- Stage 2.The height of the disc becomes even smaller, the pathological growth of cartilage tissue begins, protrusions (protrusions) appear. The patient feels constant pain, weakness, numbness of the face, stiffness in the neck and back.
- Stage 3.The fibrous ring surrounding the core of the disc breaks down and an intervertebral disc herniation occurs. The spine is noticeably deformed, increasing the risk of vertebral dislocation and subluxation. The pain is permanent and is accompanied by other symptoms of osteochondrosis.
- Stage 4.Irreversible changes occur in the spine: bone growths appear, the intervertebral disc is replaced by scar tissue and loses its ability to absorb the load. Symptoms become acute and significantly affect the patient's lifestyle and well-being. The quality of life decreases.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis requires an integrated approach, there are types of non-drug, drug and surgical treatment.
Depending on the clinical situation, the following are used:
- Massage (specialized to remove spasms and blocks, neurological);
- therapeutic exercise (to improve blood circulation);
- Osteopathy (thanks to this procedure, blocks and spasms are removed, blood circulation is restored and metabolic processes of the brain are improved);
- Manual therapy;
- Computer traction;
- Physiotherapy.
Non-drug treatmenthelps reduce the severity of symptoms and reduces the frequency and severity of exacerbations, improves blood supply to the affected area, strengthens metabolism and regeneration processes.
- Strengthens the effect of drugs;
- Helps to strengthen the muscle frame and stabilize the spine;
- Eliminates spasms and muscle blocks
Non-drug treatment also includes the wearing of Schantz splints.
Punch wheel
Shants splint or Shants collar is a soft bandage of some degree of fixation of the cervical spine, used for the prevention and treatment of injuries and diseases of the cervical spine. Field of application: emergency and urgent medical care in case of traffic accidents, injuries at home and at work, treatment of patients after surgical interventions on the cervical spine.
According to the design, Shants splint can be rigid, semi-rigid, ring-shaped, with fasteners or without fasteners, but all of them are removable and easily replaced, easy to use and maintain, affordable and have a modern design that plays an important role. the role of wearing around the neck during rehabilitation or outpatient treatment.
Drug treatmenthelps to relieve pain, get rid of dizziness, restore normal activity of nerve roots and, if possible, stop or slow down the destruction of cartilage tissue.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (aimed at relieving pain and inflammation) are used in the form of tablets, injections, ointments, patches;Muscle relaxants: drugs that eliminate reflex muscle spasms, thereby reducing pain and improving blood circulation;B vitamins in the form of a tablet, it helps to improve the conduction of nerve impulses;Chondroprotectors: drugs that promote the regeneration of cartilage tissue.
Depending on the symptoms, drugs that improve microcirculation in cerebral vessels, drugs that prevent nausea and dizziness, etc.
Surgery
The help of surgeons is necessary in advanced cases of the disease, when medical methods are no longer effective.
Surgical removal of a herniated disc (microdiscectomy, endoscopic or transfacet surgery);Laminectomy: removal of spinous processes or vertebral arch, thereby reducing the load on the spinal cord;Nucleoplasty: removal of hernias by removing part of the core of the intervertebral disc.
Prevention of osteochondrosis
- Avoid physical inactivity and lead an active lifestyle;
- Diversify your diet with foods rich in potassium and magnesium;
- Minimize heavy loads;
- sleeping on anatomical pillow and anatomical mattress;
- Warm up regularly.
Frequently asked questions
How to understand that osteochondrosis of the cervical spine has begun?
- headache
- Restriction of head rotation
- Violation of concentration
- Noise in the ears
- Dizziness
How to make a diagnosis?
- Only a doctor can make a diagnosis
- MRI, MSCT
How to relieve pain with cervical osteochondrosis?
If you have pain in the cervical spine, you should see a doctor. The doctor can prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, antispasmodics and other drugs with an analgesic effect.
How to prevent osteochondrosis?
- Start an active lifestyle
- Do preventive exercises every day (at least 10 minutes a day)
- Develop a daily routine
- Neck massage (2 times a year)
Which doctor treats osteochondrosis of the cervical spine?
First of all, you should visit a general practitioner who will give a referral for the necessary examinations and make a preliminary diagnosis. As a rule, patients with a confirmed diagnosis of osteochondrosis should consult a neurologist.































